Lead exposure – how to reduce your risk
Lead is a naturally occurring metal that has been used in many products. People can be exposed to lead in the environment when:
- it is released into the air,
- they come into contact with lead dust on surfaces
- they consume contaminated food or water.
Environmental lead levels vary around Western Australia based on what is naturally present in the soil, the age of a home, previous land uses, proximity to locations where lead is mined, refined, or used in business or hobbies. For example higher lead levels exist at some locations where historical mining and refining occurred, such as at Northampton, near foundries, shooting ranges, lead lighting workshops and battery repair shops.
Lead is mainly absorbed into the body from eating or inhalation of dusts.
Read more about lead exposure.
It is important to take care of yourself and family by reducing the risk of lead exposure.
Diet and nutrition
Diet can have a major impact on how much lead is absorbed into the body. Consuming a balanced diet and forming healthy eating habits can help minimise the absorption of lead into the body.
Eat plenty of healthy food
- Do not eat or drink after working with lead or materials containing lead, until you have thoroughly washed your hands.
- Do not use pottery or ceramic products purchased overseas unless you are certain they are safe for storing or cooking food. These products may be coated in lead glazes or paints which may leach lead into food.
- Eating a healthy, balanced diet with adequate levels of calcium, iron, vitamin C, zinc and magnesium helps minimise lead absorption. Good sources of iron include poultry, red meat, liver, fish, fortified cereal, cooked beans/lentils, and green leafy vegetables. Milk, cheese and yoghurt are good sources of calcium.
- Avoid high fat diets as they increase lead absorption.
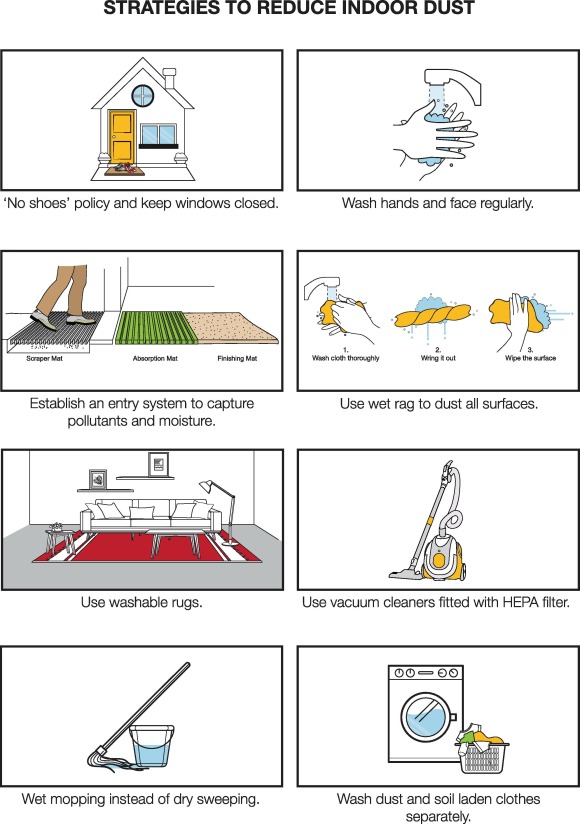
Tips for a clean and healthy home
Small quantities of fine lead particles can be present in household dust from the general outdoor environment. Levels may be higher if you undertake any activities which may release lead containing dusts. Take precautions to minimise exposure to dust in the home.
- Avoid walking dust or dirt into your home by placing durable mats at all entrances. Regularly clean the mats.Leave work boots and yard shoes outside.
- Develop good habits by washing hands whenever you:
- come inside from the garden or have been playing outside
-
before you eat or drink
-
after touching pets.
- Hand to mouth activity is more common in young children and regular handwashing is recommended. Use soap and water to wash hands. Make sure hands are dry after being washed as damp hands will pick up dust. Regularly brush under fingernails and keep them neat and short. Please be aware that hand sanitiser does not remove physical or chemical contaminants.
- Always remember to wash all fruit and vegetables thoroughly before eating or cooking
- Wash and brush family pets outside on a regular basis to minimise the amount of dust coming in on their fur.
- Use vacuum cleaners fitted with high efficiency particulate air (HEPA) filters to prevent dust being re-released back into your home.
- Regularly damp mop and wet wipe hard surfaces, bench tops, furniture, toys and windowsills.
- Wash children’s toys thoroughly with soapy water if they have been outside, especially toys and dummies (pacifiers) that are likely to be put in a child’s mouth.
- Clean air conditioner intakes and filters regularly, following the manufacturer’s instructions, taking precautions to minimise release of dusts to atmosphere.
- Seal cracks in the ceilings of older homes.
Painting, renovating and hobby activities
When painting, renovating or disposing of items containing or contaminated with lead, clean and dispose of materials safely to prevent lead exposure for you and your family.
A number of DIY activities and hobbies involving lead containing materials can increase levels of lead in fumes and dusts, activities include:
- shooting
- pottery glazing
- lead lighting
- diving in residential pools with a lead containing weight
- house renovations
- car engine maintenance
- making lead sinkers
- panel beating or other body work on cars and boats
- sanding or stripping old paint
- spray painting cars and boats
- heating, burning, flame cutting, melting, grinding or sanding any other products which contain lead.
Preparation before undertaking any hazardous activities
- Use an area which can be isolated and readily cleaned.
- Restrict access if possible.
- Ensure the area is well-ventilated and wear a respirator fitted with suitable filters when heating, welding, flame cutting or burning products which could contain lead. Different filters and respirators are available which protect from dust or fumes; choose one that complies with Australian Standard 1716 and is appropriate for the task.
- Do not walk lead dust or dirt into your home. Place durable mats at all entrances which are regularly cleaned, and leave work boots and yard shoes outside.
- Do not take contaminated clothing into the house. Remove as much dirt and dust as possible from clothes. Isolating contaminated clothes by keeping them in a plastic bag until they are washed will minimise spreading the lead to other surfaces. Wash and rinse contaminated clothing separately.
Painting and renovating
- Seek professional advice on the most appropriate and safe methods of renovating an old house/removing old paint.
- Test old paint for lead concentration before starting any renovations. Test kits are available from hardware stores.
- Use chemical paint strippers instead of blow torches or sandpaper when removing old paint which might contain lead. Chemical paint strippers can themselves be very toxic, so read the label and follow all safety directions.
- Consider painting over old lead paint if renovations cannot be carried out without generating a lot of dust and fumes.
- Do not renovate when children are present. Consider temporarily covering old paint until renovations can be completed without children present.
A booklet titled Lead Alert: A six step guide to painting your home (external site) contains information about the safe and appropriate methods of handling lead compounds and lead containing material.
Cleaning or disposing of items containing or contaminated with lead
- Thoroughly clean areas contaminated with lead paint flakes or lead dust and use a wet rag or mop and discard after use.
- If vacuuming lead dust use an industrial Class H, High Efficiency Particulate Air (HEPA) vacuum cleaner to prevent dust being rereleased into the environment.
- Place used HEPA filters, vacuum bags, dust and waste materials into a sealed plastic bag. Do this outside and place the waste in an external bin.
- Cover or seal lead tailings or contaminated soil. Depending on the location and how often the area is used, consider sealing the contaminated area with concrete, paving, gravel, clean fill or planting grass to restrict contact with your family and pets.
- Do not store old car batteries, radiators or lead flashing in or around your house. Contact your local government waste management department (external site) for further information on recycling and the safe disposal options.
- Do not burn painted wood.
Where to get help
- See your doctor.
- Ring healthdirect on 1800 022 222.
- Call the Poisons Information Centre on 13 11 26 (24 hours a day) if you suspect poisoning.
- For information on exposure at work contact WorkSafe Customer Help Centre on 1300 307 877 or to report an incident call 1800 678 198.
- Contact the Environmental Health Directorate by call (08) 9222 2000 or email DOH.chemicalhazards@health.wa.gov.au
Last reviewed: 26-10-2023
Acknowledgements
Public Health
This publication is provided for education and information purposes only. It is not a substitute for professional medical care. Information about a therapy, service, product or treatment does not imply endorsement and is not intended to replace advice from your healthcare professional. Readers should note that over time currency and completeness of the information may change. All users should seek advice from a qualified healthcare professional for a diagnosis and answers to their medical questions.